Within ScenarioContext in SpecFlow, there are two distinct ways to share data between steps in a scenario: context injection and current injection. Both approaches accomplish the same goal, but they are implemented differently.
ScenarioContext.Current:
A static attribute of the ScenarioContext class in SpecFlow is
called ScenarioContext.Current. It offers a method for storing and retrieving
data from various steps in the same scenario.
By putting values in the scenario context during one step and
retrieving them in another, you can use ScenarioContext.Current to communicate
data between steps.
Example:
While ScenarioContext.Current is convenient, it has some
drawbacks, such as being static and potentially leading to difficulties with running scenarios in parallel.
Therefore, with SpecFlow 3.0, ScenarioContext.Current
is marked obsolete.
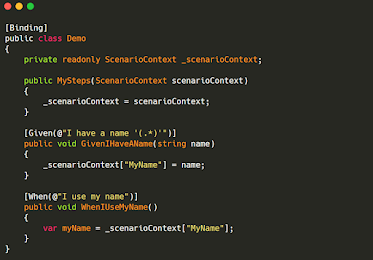
Context Injection:
Context injection allows
you to use the step class's constructor to directly inject the scenario
context. The dependency injection method in SpecFlow is used to do this. These
objects' lifespan is restricted to the duration of a scenario.
Example:
Context injection is generally considered a more modern and
flexible approach, especially for larger and more maintainable test suites.

Comments
Post a Comment